Depreciation is a topic that is new and generally difficult for aspiring Chartered Accountant students—especially those who are from the Science and Arts field. Even students from the commerce field who are already familiar with the basic meaning and knowledge of Depreciation are introduced to some new and higher-level concepts of this topic in the CA Foundation level.
You need a complete preparation strategy to complete the syllabus on time because the CA Foundation Exams dates are around the corner.
The Depreciation topic can be confusing, and it is of utmost importance that you clear your basics for this chapter. Therefore, in this article, we at CA Wizard are introducing you to the basics of the CA Foundation Depreciation chapter with flow charts and links to additional resources and practice questions.
Before we continue further, you should see this overview of the chapter.
[CTA_ca_foundation_banner_box_shortcode]
Overview
‘Depreciation’ is a topic that comes under the CA Foundation Syllabus of Paper 1- Principles and Practice of Accounting. A complete chapter is based on this particular topic, i.e., Chapter 5 Concept and Accounting of Depreciation.
Since this topic is under Paper 1 of the CA Foundation course, it has no MCQs and negative markings. Because, as per the latest CA Foundation Exam Pattern given by the Institute of Chartered Accountant of India, this paper is a completely subjective type of paper. Along with Ch 2, 3, and 4, Ch 5- Depreciation makes Section- II of Paper 1. Section-II carries 25%-30% of the weightage in the 100 marks paper.
CA Foundation Depreciation Syllabus includes the different methods of depreciation, how it is computed, treated, and shown in the Financial Statements.
Now, let’s start from the beginning and understand the concept of depreciation.
Also, See CA foundation preparation strategy.
What is Depreciation, and why is it applied?
A business has various fixed assets like property, plant and machinery, furniture, etc. which are used for daily operations and to earn revenue until they lose value and have to be sold or discarded. At the time of purchase, the value of these fixed assets is recorded at its original purchase price. However, due to the decrease in their value over their useful life, their residual price does not remain the same. Therefore, the cost of acquisition is treated as an expense every year and is deducted from the value of assets. This cost, which is decreased from the value of assets, is called DEPRECIATION.
Do you wonder why the concept of depreciation exists?
➤ See this example:
You purchased a new machine (fixed asset) worth Rs. 1,00,000 for your business. After four years, even after getting repairs, you are facing problems in the working of machinery. You decide that your machine can still work after a complete repair and wish to sell it in the market. But nobody will give more than Rs. 20,000 for an already used and partly damaged machine, right? Because it’s value has decreased.
However your accounting books still show the cost of machinery, and if you sell it at Rs. 20,000, it will be a loss of Rs. 80,000 to your business in a single year. But did you use your machine for a single year or four years?
Don’t you think that since the machine was used for four years, this loss should also be charged from each year?
To divide this loss in the useful life of an asset, depreciation is charged on the original value of the asset.
How and why the value of assets is decreased?
- Wear and tear of the asset due to constant use
- With time, the asset gets deteriorated
- Obsolescence
- Permanent decrease in the market value of the asset
- Depletion (in case of mines, oil-wells and other natural reserves)
Characteristics of Depreciation
- It is the fall in the value of the asset
- It is permanent in nature
- It is a gradual and continuous process
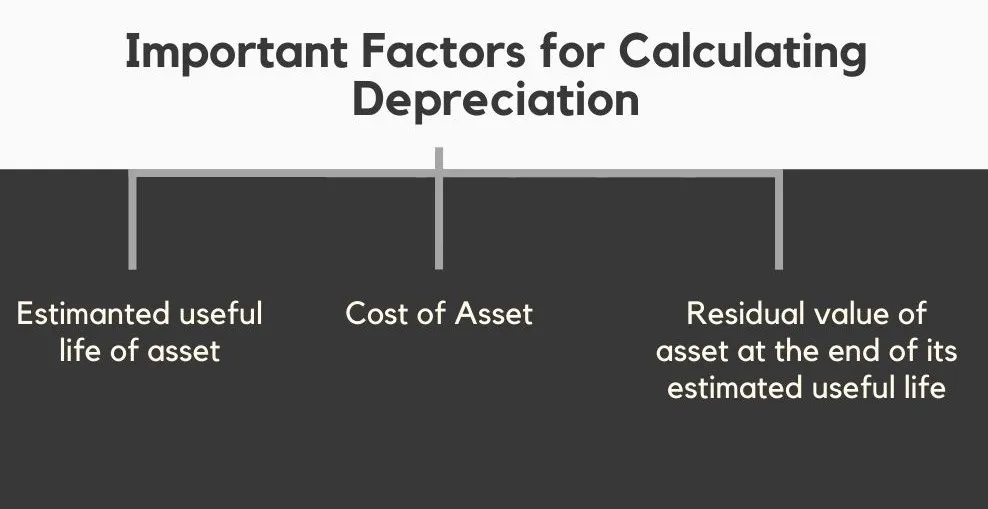
Important Factors for Determining Depreciation
These three factors are used to determine the value of Depreciation:
Objectives of Providing Depreciation
The key reasons why every business calculates the yearly amount of depreciation and why it matters to them are listed below.

Methods of Providing Depreciation
The following are the methods of calculating/determining depreciation amounts on fixed assets that are covered under the CA Foundation Depreciation chapter.
➤ Straight-line method
➤ Diminishing balance method
➤ Sum of years of digits method
➤ Annuity method
➤ Sinking funds method
➤ Machine hour method
➤ Production unit’s method
➤ Depletion method
Below we have given a gist for each method of depreciation. Before starting the detailed study, you can read and understand the brief of the whole concept of the CA Foundation Depreciation chapter. This will make it easy for you to study it in detail.
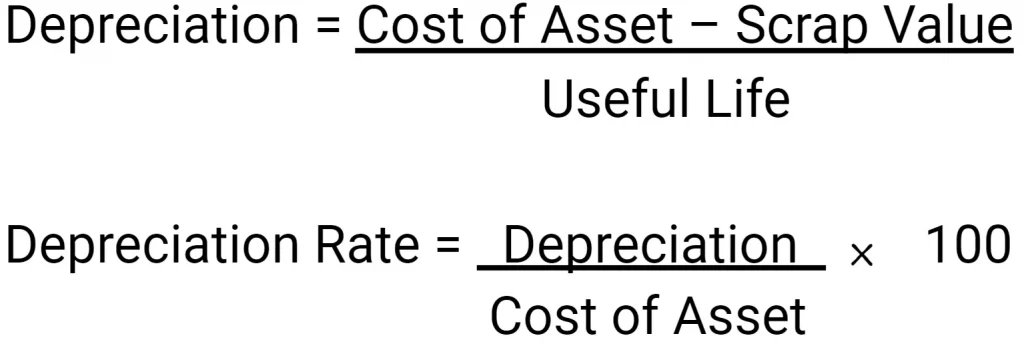
Straight Line Method:
This method is also known as the ‘Equal Instalment Method’ because an equal amount of depreciation is written off every year until the end of the working life of an asset. According to this method, the following formulas are used to find the depreciation amount and rate.
Reducing/Diminishing Balance Method:
A fixed percentage is written off under the diminishing balance method. However, the value of depreciation decreases every year. This method is also called the Written Down Method and Reducing Balance Method.
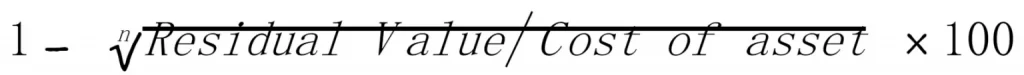
Sum of Years of Digits Method:
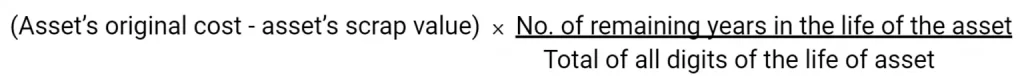
This method is a variation of the Diminishing Balance method. In this method, depreciation is calculated by this formula:
Annuity Method:
Normally we reduce the cost of the fixed asset that is used over the years from its original cost. But the annuity method considers an additional concept. It is based on the assumption—if the amount spent on the purchase of the asset was invested somewhere, the business would have earned some interest amount.
Therefore, in this method, both the loss of interest and the cost of the asset used are charged against the original value of the asset.
Sinking Fund Method:
As we mentioned above, one of the reasons for charging depreciation every year is to generate adequate funds for replacement of the asset. However, it may happen that the price of the asset is too large and the business does not have enough funds readily available to spend on the purchase of a new asset. To safeguard the business from such situations, the Sinking Fund Method is used.
In this method, the amount charged as depreciation is transferred to the Sinking Fund account and the same amount is invested in Government Securities. This way, by the time replacement of assets, needs to be made, the business will have enough funds readily available.
Machine Hour Method
The Machine Hour Method is used only when it is feasible to keep a record of the exact working hours of the machine. Thus the depreciation is calculated as per the number of hours the machine would work in its estimated useful life.

Production Units Method:
The production units method of charging depreciation is applicable on machines. The annual production is compared with the estimated total production to determine the amount of depreciation.
Depreciable Amount = Cost of Asset – Scrap Value

Depletion Method:
The Depletion Method is the last method covered under the CA Foundation depreciation chapter. It is used when the depreciation is charged for assets like mines, oil wells, quarries, or any other asset with a certain quantity of products. The depreciation for this method is calculated by the below-given formulas:

Notes
Below are some other important topics covered under the CA Foundation Depreciation Syllabus:
➤ Profit/Loss on Sale of Depreciable Asset
Whenever the asset is sold, the value of the asset after charging depreciation is used to find the profit/loss.
➤ Change in the method of depreciation and useful life of the asset should be made as per the Accounting Standards.
Now that the CA Foundation Depreciation chapter seems easy, you can dig in the details of each sub-topic. Don’t delay and download the complete notes of the Depreciation chapter now.
(You can find and download the complete notes for the CA Foundation Depreciation chapter in PDF from the CA Foundation study material . It has solved illustrations that will help you understand each concept better.)
Depreciation is an important topic, and even if you are clear with the basics, you must not neglect the detailed study of this topic.
Practice Questions for CA Foundation Depreciation Chapters- 2023
After completing the study of this chapter you should solve practice questions.
Get Complete Question Bank, Mock Test and Revision Test Papers for CA Foundation Depreciation.
Below are some practice questions taken from various papers. It will give you an idea of how depreciation questions are asked in CA Foundation papers.
Q1. Explain the difference between the straight-line method and the diminishing balance method of depreciation.
Q2. X purchased a machinery on 1st January 2018 for Rs. 4,80,000 and spent Rs. 20,000 on its installation. On 1st July 2018 another machinery costing Rs. 2,00,000 was purchased. On 1st July 2019, the machinery purchased on 1st January 2018 having become scrapped and was sold for Rs. 2,90,000 and on the same date fresh machinery was purchased for Rs. 5,00,000. Depreciation is provided annually on 31st December at the rate of 10% p.a. on written down value. Prepare Machinery account for the years 2018 and 2019.
Q3. A Plant and Machinery costing Rs. 10,00,000 is depreciated on straight line assuming 10 year working life and zero scrap value for four years. At the end of the fourth year, the machinery was revalued upwards by Rs. 40,000. The remaining useful life was reassessed at 8 year. Calculate depreciation for fifth year.
We hope this topic won’t make you panic anymore and looks easy to study. You can try these easy tips to balance your study time table and give time to all subjects and topics of the CA Foundation.
You can also join online CA classes from the best Coaching Institute for future Chartered Accountants. The right faculty can help you achieve your dream and clear the CA Foundation Exam.
Prepare well and do well in the CA Foundation Exam Preparations. All the best!
Also, check about:- The CA foundation Sure Success tips.









